Speakers are usually able to accept quite high impulse power and measuring of speaker distortion by sine bursts would show if we are still in relatively linear region. The pain of sine burst distortion measurement is in length of the burst, which may not be long enough to get sufficient resolution for spectrum analysis. I tried to make a compromise – test signal is a sine burst at 100Hz frequency, 20 periods, amplitude shaped by Blackmann window. The first results look promising.
The test burst had voltage amplitude of 30.3Vpeak, that means 21.4Vrms of equivalent sine wave. This would be 76W at 6ohm load impedance. The woofer measured was 6.5” Seas W18NX001 and 21.4Vrms of steady state 100Hz sine would be impossible to apply. Speaker input voltage and acoustical output were recorded to left and right channel of the wav file. Distortion was estimated by post-processing of the recorded file. The result is interesting – voltage distortion at speaker terminals is about 0.02% and distortion on acoustical side is about 2%, which is much less than I was expecting from measurements with steady state sines.
Measured burst shapes are attached as well as distortion measured.
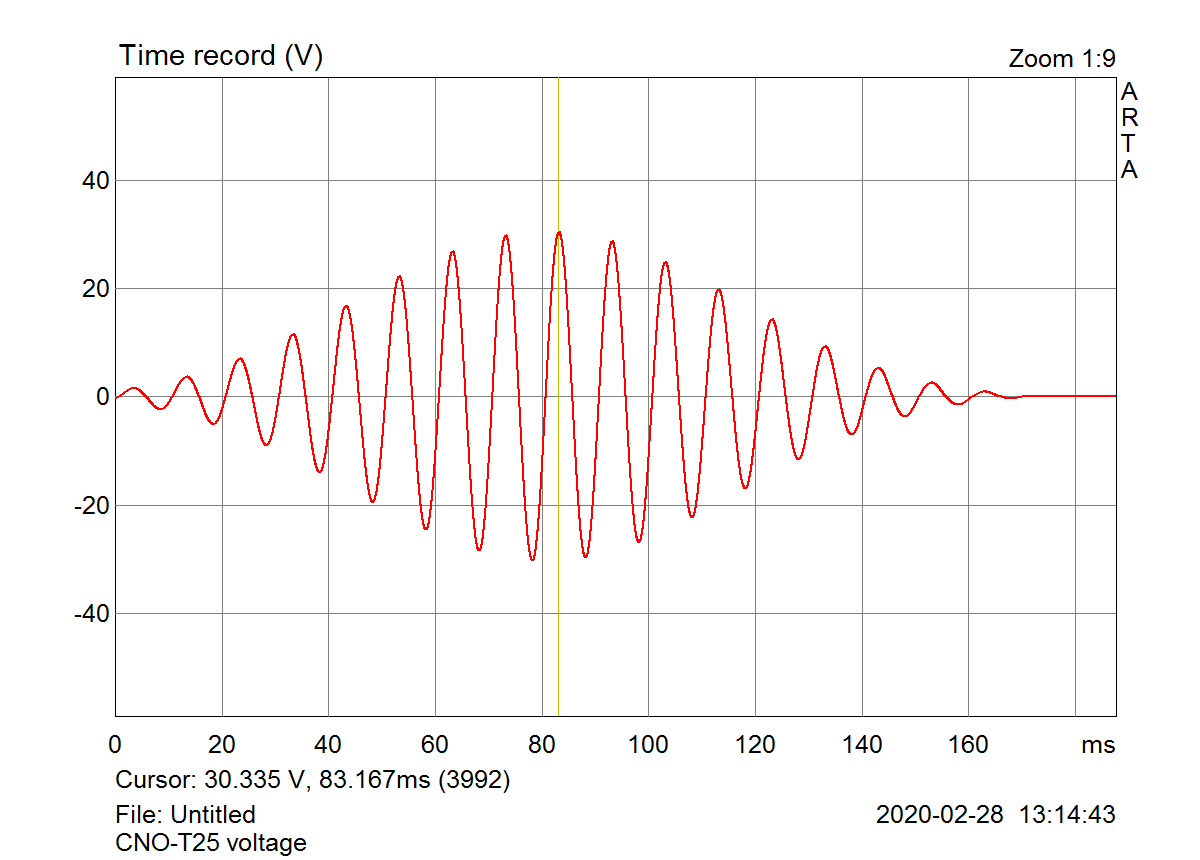
Burst voltage at speaker terminals
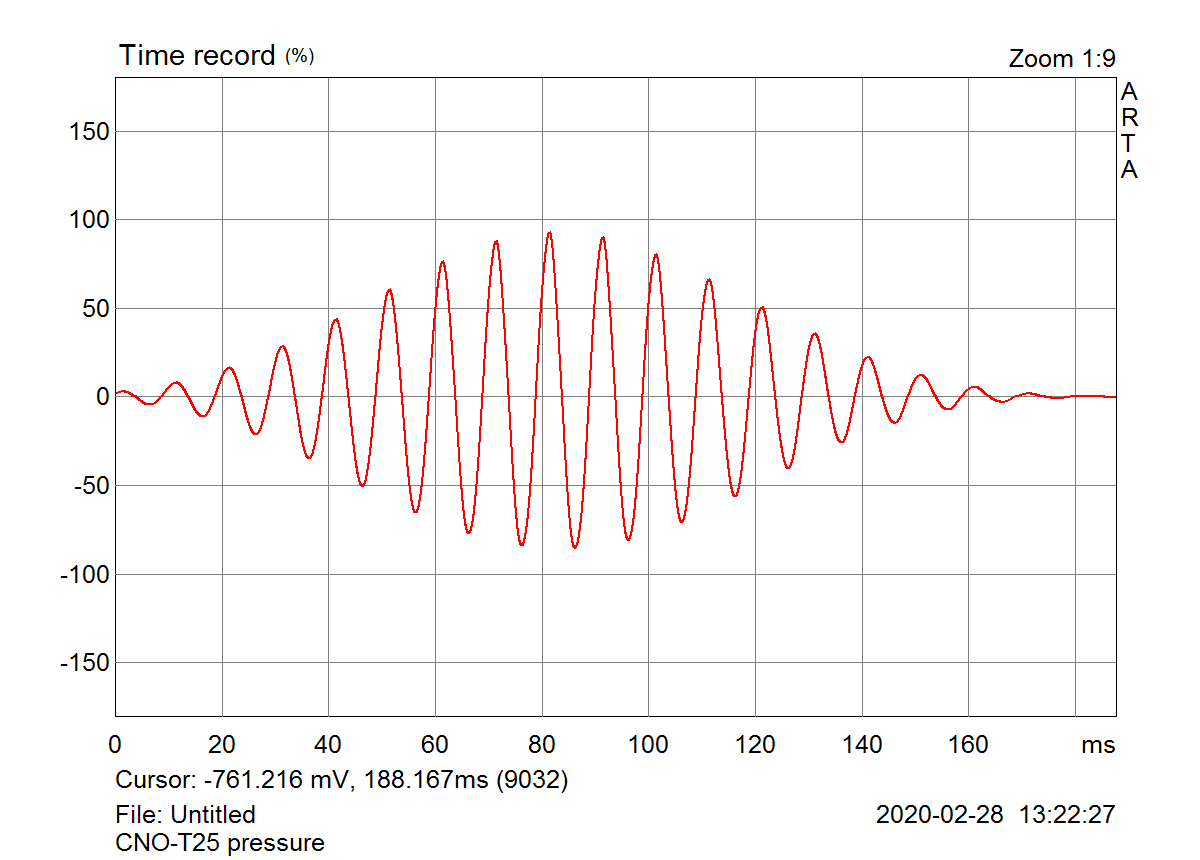
Burst measured at acoustical side
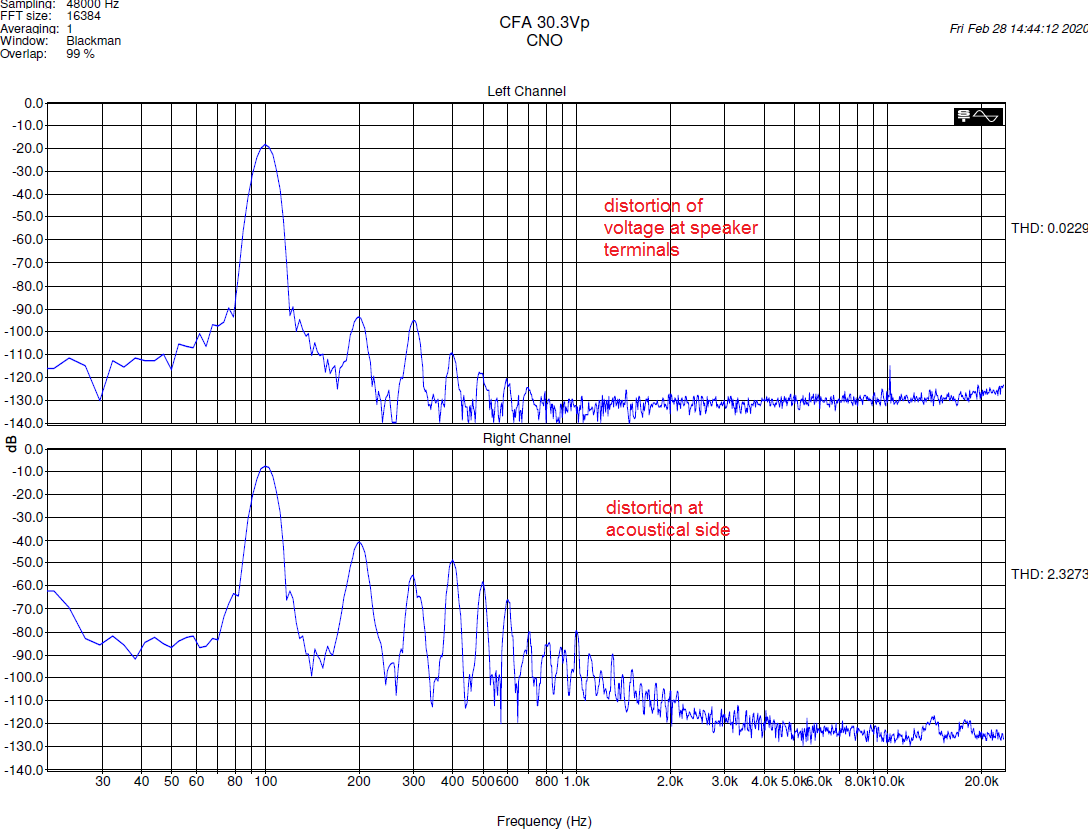
Distortion at electrical and acoustical side
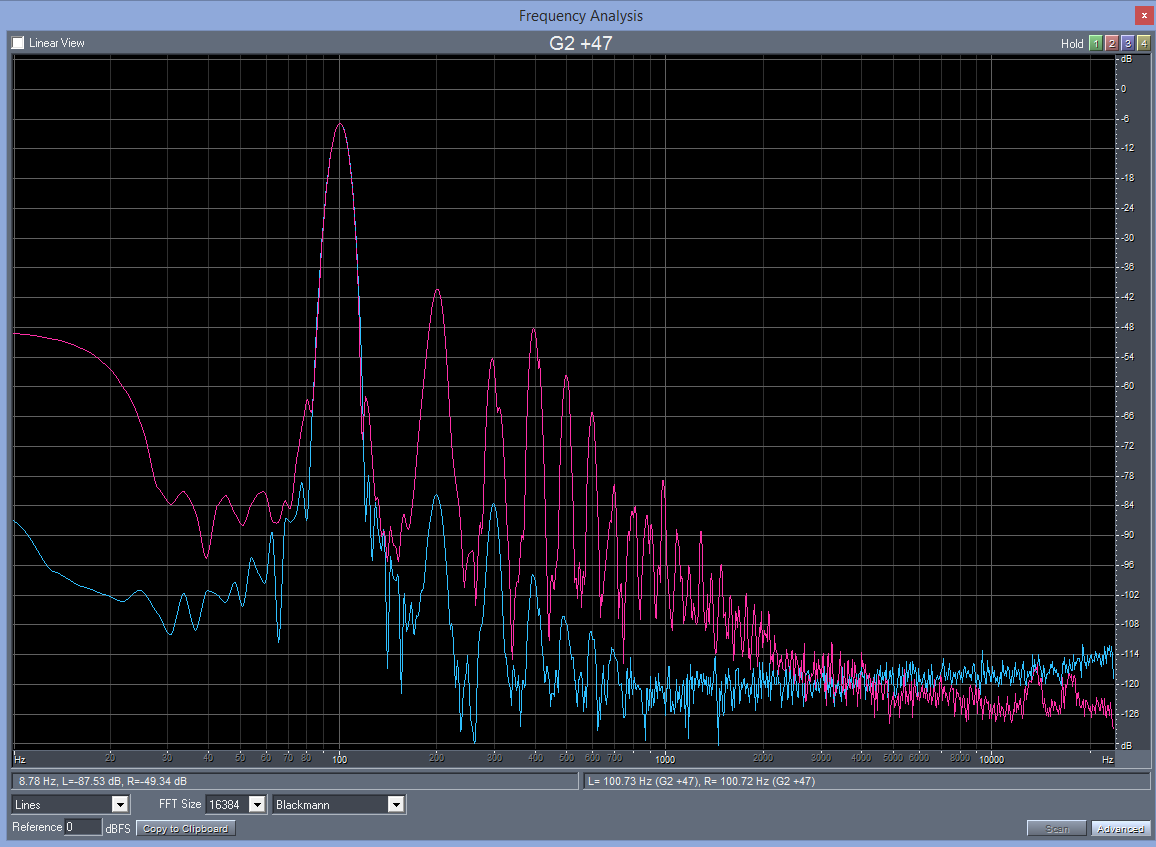
Distortion plots with levels equalized. Blue - electrical distortion, red - acoustical distortion. Electrical recording was lower in level, it had to be amplified of 11dB to equalize levels, which can be seen in higher noise floor above 3kHz.
The test burst had voltage amplitude of 30.3Vpeak, that means 21.4Vrms of equivalent sine wave. This would be 76W at 6ohm load impedance. The woofer measured was 6.5” Seas W18NX001 and 21.4Vrms of steady state 100Hz sine would be impossible to apply. Speaker input voltage and acoustical output were recorded to left and right channel of the wav file. Distortion was estimated by post-processing of the recorded file. The result is interesting – voltage distortion at speaker terminals is about 0.02% and distortion on acoustical side is about 2%, which is much less than I was expecting from measurements with steady state sines.
Measured burst shapes are attached as well as distortion measured.
Burst voltage at speaker terminals
Burst measured at acoustical side
Distortion at electrical and acoustical side
Distortion plots with levels equalized. Blue - electrical distortion, red - acoustical distortion. Electrical recording was lower in level, it had to be amplified of 11dB to equalize levels, which can be seen in higher noise floor above 3kHz.